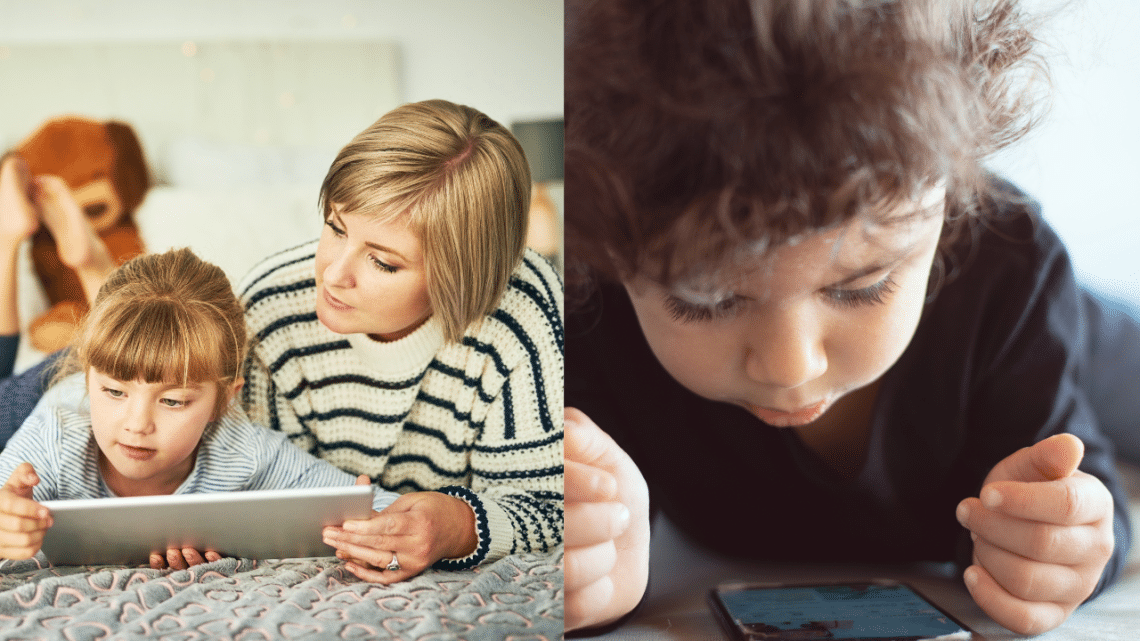
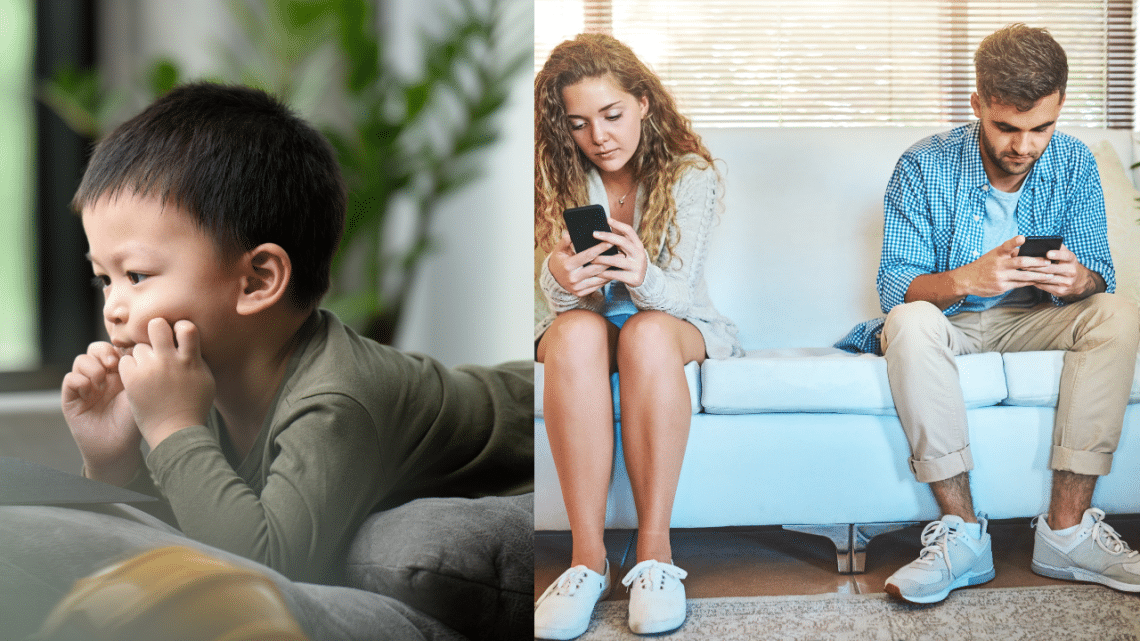
Excessive screen time has become a significant concern, impacting mental health across all age groups. From children to adults, the effects of prolonged device usage are profound, affecting various aspects of well-being.
Peter Hans, the President of the University of North Carolina System, highlights the detrimental impact of smartphones on college students in his opinion piece. He echoes the concerns raised by social psychologist Jonathan Haidt, who attributes the decline in mental health among Gen Z to the advent of smartphones, replacing essential childhood experiences with screen time.
Hans emphasizes the importance of fostering resilient, open-minded exploration among students, a goal hindered by excessive smartphone use. He notes the rise in demand for counseling, psychiatric disorders, and concerns about student safety as direct consequences of this trend.
To address these issues, Hans proposes various solutions, including raising the age of first access to smartphones, limiting social media usage, and removing phones from classrooms. He also advocates for universities to uphold their role as counter-cultural havens, promoting real-world social connections and deep thinking.
Ultimately, Hans argues for a reevaluation of priorities, encouraging students to recognize the value of their time and seek higher forms of happiness beyond the digital realm.
The insights presented above are drawn from Peter Hans’s opinion piece published on the Charlotte Observer’s website, authored by Peter Hans
Physical and Mental Health Concerns
The effects of screen time on mental health are well-documented. Excessive device usage has been linked to anxiety, depression, and decreased self-esteem, particularly in children and adolescents. Constant exposure to screens, especially social media platforms, can lead to feelings of inadequacy, comparison, and cyberbullying, contributing to psychological distress.
Prolonged screen time often leads to a sedentary lifestyle, contributing to health problems like obesity, poor posture, and disrupted sleep patterns. Lack of physical activity due to excessive screen time can weaken muscles, affect cardiovascular health, and increase the risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
Social Interaction and Cognitive Development
Excessive device usage can hinder face-to-face social interaction skills, leading to difficulties in forming meaningful relationships and communication problems. Children and adults who spend too much time on screens may experience social withdrawal, loneliness, and a reduced ability to empathize with others, impacting their overall well-being.
For children, the effects of screen time on cognitive development are particularly concerning. Too much screen time can interfere with attention span, problem-solving abilities, and creativity. Excessive exposure to screens, especially during critical developmental stages, may impede brain development and hinder the acquisition of essential skills necessary for learning and social interaction.
Blue Light Effects and Digital Addiction
The blue light emitted by screens can disrupt sleep patterns by interfering with the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep. Prolonged exposure to blue light, especially before bedtime, can delay the onset of sleep, reduce sleep quality, and lead to fatigue and daytime drowsiness, impacting overall health and productivity.
Excessive screen time can lead to addictive behaviors, where individuals struggle to control their usage despite negative consequences, similar to other forms of addiction. Children and adults may experience withdrawal symptoms, cravings, and compulsive urges to check their devices, leading to decreased productivity, academic or work performance, and overall life satisfaction.
Parental Role and Mindful Device Usage
Parents play a crucial role in managing their children’s screen time by setting limits, providing alternative activities, and being good role models themselves. Establishing clear rules and boundaries around screen time usage, fostering open communication, and monitoring online activities can help mitigate the effects of excessive screen time on children’s health and well-being.
Encouraging mindfulness and setting boundaries around screen time can help individuals, both children and adults, develop healthier relationships with technology. Practicing mindfulness techniques such as mindful breathing, digital detoxes, and scheduled screen-free time can promote greater awareness of screen time habits, reduce dependency on devices, and improve overall mental and emotional well-being.
Emphasizing a Balanced Lifestyle
It’s essential to emphasize the importance of a balanced lifestyle that includes physical activity, social interaction, and time spent outdoors, alongside screen time. Encourage individuals to engage in a variety of activities, such as sports, hobbies, and outdoor adventures, to promote physical health, social connections, and personal fulfillment, while also enjoying the benefits of technology in moderation.
Educational Use vs. Entertainment
Not all screen time is created equal; there are educational benefits to technology when used in moderation and with purpose. Screen time can enhance learning experiences, stimulate curiosity, and provide access to valuable resources and educational content. However, it’s essential to balance educational screen time with other activities and monitor content to ensure it aligns with learning objectives and promotes positive development.
Reach out to us, and we’ll be delighted to assist you. Stay tuned for all updates! Follow us on social media, Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube.
.
.
.
.

Top Charlotte Real Estate Agent As Seen on House Hunters Charlotte guiding her buyer Lyndsay on her relocation.
Charlotte Real Estate Agent
Danielle Edwards
danielleedwards@REMAX.net
704-604-2999